(Originally posted Dec 13, 2017; last updated on July 9, 2024)
In some jurisdictions it is possible to withhold information from a Safety Data Sheet that identifies product recipes or other proprietary details which, if revealed to others, could be detrimental to your business interests. The UN GHS specification, European Union (EU/EEA) regulations, and Canadian regulations refer to company-proprietary details as Confidential Business Information (CBI). US-OSHA regulations use the term specific chemical identity as it pertains to substances or product ingredients.
This post summarizes the requirements for withholding confidential information from SDSs in the USA, Canada, EU/EEA, and Korea.
USA (US-OSHA)
For the US, the Hazard Communication Standard (HCS, or "HCS 2024") allows you to claim a trade secret for chemical name(s), other specific identification of a hazardous chemical, or the exact percentage (concentration) of substance(s) in a mixture (29 CFR 1910.1200(i)1). You can make this claim without prior approval from OSHA, although you should be prepared to justify the claim if asked to do so. Additional requirements for claiming trade secrecy include:
A statement that you have made a claim of trade secrecy, indicating that the specific chemical identity and/or exact percentage of composition is being withheld as a trade secret. (In SDScribe™, this statement occurs in Section 3, Composition.)
The SDS must still include the properties and effects of the hazardous chemicals for which you are withholding the chemical identity and/or exact concentration.
If the concentration or concentration range is being withheld as a trade secret, then the SDS must include a prescribed concentration range instead, using the narrowest range of the following:
0.1% to 1%
0.5% to 1.5%
1% to 5%
3% to 7%
5% to 10%
7% to 13%
10% to 30%
15% to 40%
30% to 60%
45% to 70%
60% to 80%
65% to 85%
80% to 100%
(These ranges are the same as used by Health Canada, as discussed below.)
You can combine two adjacent concentration ranges if the exact concentration is between 0.1% and 30%, and does not fit entirely into one of these ranges. For example, if the ingredient’s actual range is 0.9 to 2 percent, the SDS could indicate 0.5 to 5 percent (two adjacent ranges)
You can also use a range that is narrower than the prescribed range or combination of two adjacent ranges. For example, for the ingredient with an actual range is 0.9 to 2 percent, the SDS could indicate 0.9 to 5 percent, or 0.5 to 2.5 percent. This provision allows the manufacturer/distributor some flexibility if using the prescribed range would trigger other requirements, such as in shipping or storage.
You should have a concentration or concentration range for each hazardous ingredient. You cannot use a value of zero, have a concentration range that includes zero, or omit the concentration entirely.
You must disclose the specific chemical identity and concentration in cases of medical emergencies, medical treatment for exposed individuals, workplace monitoring, and the evaluation of suitable protective equipment to prevent harmful exposures. The HCS identifies specific circumstances and requirements for persons requesting the information.
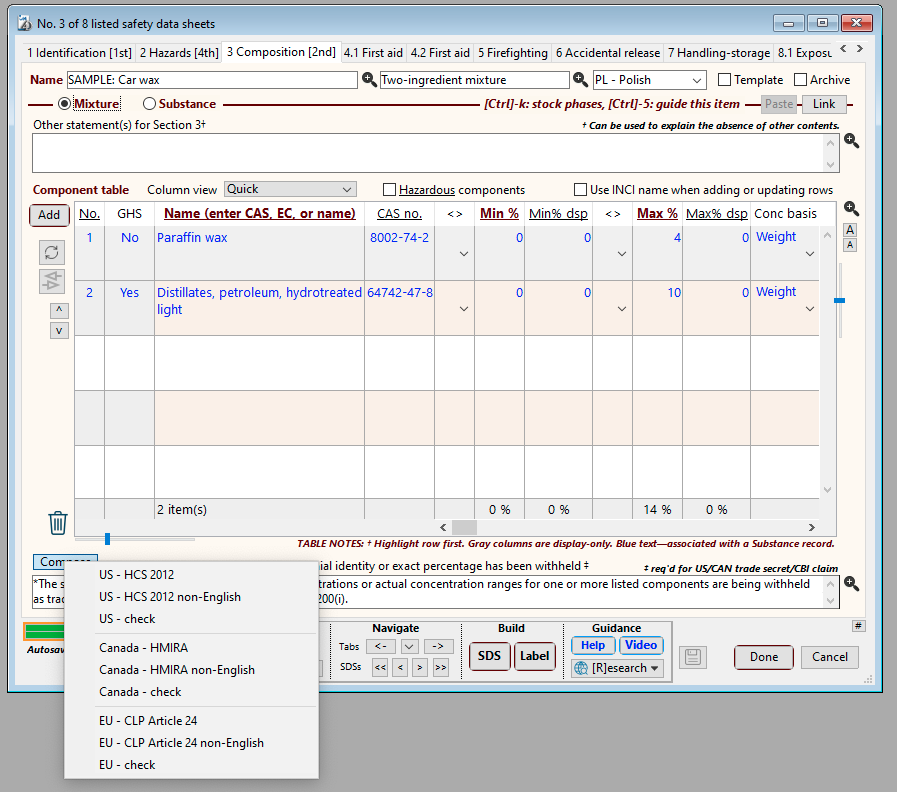
SDScribe™ has a Component table in SDS Section 3 (Composition), where each row represents an ingredient, stabilizer, impurity, or other component of the product which (at its concentration in the product) contributes to the hazards associated with the product as a whole. As an option, you can also include non-hazardous items, and/or hazardous items present below thresholds levels in the product.
SDS tab “3 Compositon”, showing the Component table. The Min% and Max% columns allow you to select the actual concentration or actual concentration range for each ingredient. The Min% dsp and Max% dsp columns allow you to enter the concentration or concentration range you wish to appear on the SDS.
Also shown are the options from the Compose button (below the Component table), which can generate statements for claiming trade secrecy/confidential business information (CBI) related to ingredients. The Compose button includes diagnostic options (“ - check”) to verify consistency for CBI claims.
For the HCS, you omit the specific chemical identity of a hazardous ingredient by checking the box in the "Name w/h" column, for the ingredient row. When generating the SDS, the program will replace the ingredient name with the phrase "Component x (trade secret)*", where "x" is the position of the ingredient in the table. You can use the trailing asterisk (*) on this phrase to reference the trade secret claim statement, which is located just below the Component table.
Name w/h column in the Component table, which in the “Quick” column view appears further to the right of the concentration columns. Checking the box for a row causes the program to use “Component x (trade secret)*” on the SDS for the actual chemical name of the ingredient.
The Component table contains minimum and maximum percentage columns (“Min%” and “Max%”, respectively), for specifying the concentration range for each ingredient. If you plan on using an actual, single concentration for an ingredient, then use only one of the columns (minimum or maximum) for the concentration value.
The Component table also has minimum and maximum percentage columns for display on the SDS (“Min% dsp” and “Max% dsp”, respectively). If these columns contain concentration values, then they will appear on the SDS instead of the actual minimum/maximum percentage values. As a convenience, clicking on the “Min% dsp” column header when a row is highlighted allows you to select a prescribed concentration range for that row.
Clicking on the header of the Min% dsp column enables convenient selection of a prescribed concentration range, which the program will insert as two values, into the Min% dsp and Max% dsp columns.
Because SDS Sections 8 (Exposure-protection), 11 (Toxicological), 12 (Ecological), and 15 (Regulatory) may also contain references to specific chemical names of ingredients, the program offers an option to substitute "Component x" for the actual chemical names in these sections, when you generate the SDS. When SDS generation is complete, ensure that you proofread these sections. The program won't distinguish between, say, "sodium hydroxide" and "sodium hydroxide carbonate" in the text of these sections – your SDS might contain references to "Component 3 carbonate". You may also need to manually remove references to CAS numbers, EC numbers, or other chemical identifiers.
Planning for multiple markets
Generally, the US has the most permissive regulations regarding trade secrecy claims on safety data sheets. Taking full advantage of these provisions may be problematic for companies with multi-national product distribution, however, since ingredients and/or concentrations withheld on a US SDS may need to appear on SDSs in other countries or regions. Thus US customers may be dissatisfied if they find better information on non-US SDSs for the same product.
Canada (Health Canada)
Canada regulates CBI claims under its Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS 2015) regulations. You can read more about the specific provisions for withholding CBI here.
As with the US-OSHA HCS regulation, WHMIS 2015 permits you to withhold:
The chemical identity of an ingredient, substance, or material (including impurities and stabilizing solvents).
Actual concentration or concentration range.
The names of any toxicological study that identifies the ingredient, substance or material.
Employers can also withhold a product identifier (chemical name, trade name and/or other means of identification for the product itself); and information that could be used to identify a supplier.
Instead of using "Component x (trade secret)*" as a substitute for the actual chemical name of an ingredient (as with US-OSHA in the HCS), you would use a “code name or code number (e.g., a generic chemical name).” For example, you might use "Alcohol" as a substitute for an actual name of propanol or t-butyl alcohol.
Concentration for an ingredient can be expressed as a range (minimum to maximum) which contains the actual value or actual concentration range. Unlike the HCS requirements, WHMIS 2015 allows you to omit concentration entirely, substituting a phrase like "Proprietary*" instead.
To withhold confidential information, you must file a claim for exemption with Health Canada. The agency charges a processing fee for the claim application. You must include the code name/number you plan to use (if any) for each ingredient.
When Health Canada determines that the application is complete, it issues an HMIRA registration number and a claim filed date under the Hazardous Materials Information Review Act (HMIRA). Once you receive the HMIRA number, you can issue the Safety Data Sheet.
Health Canada will subsequently either approve or request changes to your claim. Prior to approval, Health Canada can still require you to make changes to your CBI claim, or (ultimately) to deny the claim. You have a limited time to make the requested changes on the Safety Data Sheet.
Each ingredient that has a replacement name (GCI) or a concentration substitution should refer to the HMIRA registration number and claim filed date (or the claim approval date, if Health Canada has granted the claim).
In SDScribe™, you enter the HMIRA registration number, the claim filed date, and (if Health Canada has approved the claim) the claim granted date in SDS Section 1 ("Identification").
Location for the HMIRA registration number (HMIRA RN), claim filing date (Claim filed), and claim granted date (Granted), on Tab “1 Identification” of the SDS entry form. The Show more button (top right, currently “Show less”) must be pressed to display these fields.
The Composition table has an "Alternative/generic name" column for the code name/number of an ingredient. When present, the text in this column replaces the specific chemical name, unless the "Name w/h" box is checked.
To entirely omit the concentration of an ingredient, leave the minimum and maximum concentration columns in the Component table at zero, and do not include any "less than", "greater than", etc. modifiers (e.g., "<, <=, =, >, >=") in the adjacent columns. You would then add a phrase like "Proprietary*" in the “Conc note” column.
Each ingredient (row) in the Component table for which CBI withholding applies should reference a statement (use the "Trade secret statement..." field below the table). The statement should contain the HMIRA registration number and the claim filing date (or the claim approval date, if available). The example which Health Canada uses in their fact sheet is "* HMIRA RN: 3333 – Decision Granted Date January 1, 2021".
Prescribed concentration ranges
Canada offers another option for withholding actual ingredient concentrations when they fall within specified ranges. This option does not require submission or prior approval from Health Canada, provided that you are not also planning to use generic chemical names.
A discussion of these ranges appears in a separate post, “Canada and prescribed concentration ranges”. These ranges are identical to those available in the US-OSHA HCS, discussed above.
European Union/European Economic Area (ECHA)
Similarly to the Canadian regulations, the European Classification, Labelling and Packaging regulations permit the use of an alternative chemical name for ingredients in mixtures, to replace the specific chemical identity of the ingredient.
The EU requires that you file a request to use an alternative chemical name for one or more ingredients, with the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA). You file the claim online, at the agency's web portal (REACH-IT). The claim filing process also involves creating an account there, if you don't have one already. The ECHA charges a processing fee.
Once fee payment is received, the ECHA will respond to the request within six weeks, indicating whether your choice of alternative chemical name(s) is acceptable. However, they can modify or withdraw their approval at a later date, subject to an appeals process.
The requirements for using an alternative name include:
The ingredient must not have a community workplace exposure limit from the European Agency for Safe and Health at Work.
The ingredient must fall exclusively into one or more of the following hazard classifications:
Any physical hazard
Acute toxicity, Cat. 4
Skin corrosion/irritation, Cat. 2
Specific target organ toxicity - single exposure (STOT-SE), Cat. 2 or 3
Specific target organ toxicity - repeated exposure (STOT-RE), Cat. 2
Hazardous to the aquatic environment, chronic, Cat. 3 or 4
The alternative chemical name must provide adequate information on the nature of the ingredient for handlers to take suitable health and safety precautions.
Unlike either the HCS or the WHMIS 2015 regulations, the EU CLP regulation does not provide a mechanism to file a CBI claim for ingredient concentrations.
South Korea (MoEL)
The Republic of Korea now requires manufacturers and importers of hazardous chemicals to submit safety data sheets to the Ministry of Employment and Labor (MoEL) for approval prior to product distribution. Non-Korean entities should use an “Only Representative” in Korea for this purpose.
Upon approval, the MoEL issues a serial number that must be included on the upper portion of the first page of the SDS. (SDScribe™ now provides an “SDS no.” field that can be used for this purpose; the “SDS no.” field can appear in the header of all pages.)
“SDS no.” field (upper right), on Tab “1 Identification” of the SDS entry form.
Companies wishing to claim trade secrecy for hazardous ingredients above threshold levels must obtain prior approval by submitting an application for non-disclosure to the MoEL web portal.
The application should provide the specific chemical identity and concentration for the proposed CBI ingredient(s); the hazard classification(s) for the product and for the CBI ingredient(s); the reasons for requesting CBI; and should demonstrate that the ingredient(s) are not carcinogenic, mutagenic, or reproductive toxicants (non-CMR; certain other toxic/controlled chemicals are also excluded from eligibility).
Once the application is approved, the MoEL will issue an authorization number that is valid for five years, with an additional five years available on application for an extension. The authorization number should appear in SDS Section 3. In SDScribe™, you may wish to include this number in the “Trade secret statement…” field, below the Composition table.